RealPlayer 16.0.1.18
RealPlayer 16.0.1.18
RealNetworks Inc - (Freeware)
Real Player is a program specially designed for video playback although it also contains many other useful and interesting features.
Real Player is a software program that includes the latest media player, music jukebox and listen to most common formats on the Web browser integrated multimedia.
The suite includes a multi-channel audio player, with the ability to create playlists, etc.
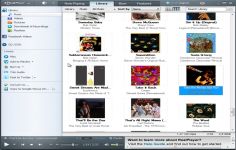
RealPlayer’s interface is pretty close to the Windows Media Player with 5 tabs available at the top of the screen, being very intuitive and easy to use. As the user quickly understood it, the first section will be the one in which it will find the media being played (either local media or online).
The library proved completely standard at the first use, it will ask the software to scan the directories to add songs to it. RealPlayer will especially look for album art on the internet. The burning functionality is supported through the library.
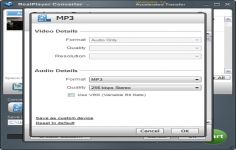
With this software it is also possible to download videos on specialized sites, format conversion of files and more.
It is also possible to convert a file from one format to another as long as user has the proper codecs. Real Player is capable of transferring video files to devices such as iPods, game consoles and other devices of its kind.
In case the user wants to raise or collect several videos, it offers all the necessary tools for this. Once the installation is finished , the user can share the video on social networks or on specialized sites for streaming video online.
- Title:
- RealPlayer 16.0.1.18
- File Size:
- 36.7 MB
- Requirements:
- Windows XP / Vista / Windows7 / XP64 / Vista64 / Windows7 64 / Windows8 / Windows8 64
- Language:
- en-us
- License:
- Freeware
- Date Added:
- 13 Mar 2013
- Publisher:
- RealNetworks Inc
- Homepage:
- http://www.real.com
- MD5 Checksum:
- 464B114947EED3161CC069E37CC692E6
# Bugs fixed:
* InnoDB Storage Engine: Raised the number of I/O requests that each AIO helper thread could process, from 32 to 256. The new limit applies to Linux and Unix platforms; the limit on Windows remains 32.
* InnoDB Storage Engine: InnoDB returned values for “rows examined†in the query plan that were higher than expected. NULL values were treated in an inconsistent way. The inaccurate statistics could trigger “false positives†in combination with the MAX_JOIN_SIZE setting, because the queries did not really examine as many rows as reported.
* Replication: When using the statement-based logging format, INSERT ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE and INSERT IGNORE statements affecting transactional tables that did not fail were not written to the binary log if they did not insert any rows. (With statement-based logging, all successful statements should be logged, whether they do or do not cause any rows to be changed.)
* Replication: Formerly, STOP SLAVE stopped the slave I/O thread first and then stopped the slave SQL thread; thus, it was possible for the I/O thread to stop after replicating only part of a transaction which the SQL thread was executing, in which case—if the transaction could not be rolled back safely—the SQL thread could hang.
Now, STOP SLAVE stops the slave SQL thread first and then stops the I/O thread; this guarantees that the I/O thread can fetch any remaining events in the transaction that the SQL thread is executing, so that the SQL thread can finish the transaction if it cannot be rolled back safely.
* DES_DECRYPT() could crash if the argument was not produced by DES_ENCRYPT().
* The server and client did not always properly negotiate authentication plugin names.
* --autocommit=ON did not work (it set the global autocommit value to 0, not 1).
* A query of the following form returned an incorrect result, where the values for col_name in the result set were entirely replaced with NULL values:
SELECT DISTINCT col_name ... ORDER BY col_name DESC;
* SHOW PRIVILEGES did not display a row for the PROXY privilege.
* SHOW PROFILE could truncate source file names or fail to show function names.
* DELETE or UPDATE statements could fail if they used DATE or DATETIME values with a year, month, or day part of zero.
* The ESCAPE clause for the LIKE operator allows only expressions that evaluate to a constant at execution time, but aggregate functions were not being rejected.
* Memory leaks detected by Valgrind, some of which could cause incorrect query results, were corrected.
* The DEFAULT_CHARSET and DEFAULT_COLLATION CMake options did not work.
* An OUTER JOIN query using WHERE column IS NULL could return an incorrect result.
* Starting the server with the --defaults-file=file_name option, where the file name had no extension, caused a server crash.
* Outer joins with an empty table could produce incorrect results.
* In debug builds, SUBSTRING_INDEX(FORMAT(...), FORMAT(...)) could cause a server crash.
* When mysqladmin was run with the --sleep and --count options, it went into an infinite loop executing the specified command.
* Some string manipulating SQL functions use a shared string object intended to contain an immutable empty string. This object was used by the SQL function SUBSTRING_INDEX() to return an empty string when one argument was of the wrong datatype. If the string object was then modified by the SQL function INSERT(), undefined behavior ensued.
* Parsing nested regular expressions could lead to recursion resulting in a stack overflow crash.
* The fix for Bug#25192 caused load_defaults() to add an argument separator to distinguish options loaded from configure files from those provided on the command line, whether or not the application needed it.
* The mysql client went into an infinite loop if the standard input was a directory.
* Outer joins on a unique key could return incorrect results.
* The expression const1 BETWEEN const2 AND field was optimized incorrectly and produced incorrect results.
* Some RPM installation scripts used a hardcoded value for the data directory, which could result in a failed installation for users who have a nonstandard data directory location. The same was true for other configuration values such as the PID file name.
* On FreeBSD and OpenBSD, the server incorrectly checked the range of the system date, causing legal values to be rejected.
* Sorting using ORDER BY AVG(DISTINCT decimal_col) caused a server crash or incorrect results.
* When using ExtractValue() or UpdateXML(), if the XML to be read contained an incomplete XML comment, MySQL read beyond the end of the XML string when processing, leading to a crash of the server.
* DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB() return a string if the first argument is a string, but incorrectly returned a binary string. Now they return a character string with a collation of connection_collation.
Related software
4.3/5 from 49 users